7. Working with the Map¶
EPANET displays a map of the pipe network being modeled. This chapter describes how you can manipulate this map to enhance your visualization of the system being modeled.
7.1. Selecting a Map View¶
One uses the Map Page of the Browser (Section 4.7) to select a node and link parameter to view on the map. Parameters are viewed on the map by using colors, as specified in the Map Legends (see below), to display different ranges of values.
Node parameters available for viewing include:
- Elevation
- Base Demand (nominal or average demand)
- Initial Quality (water quality at time zero)
- *Actual Demand (total demand at current time)
- *Hydraulic Head (elevation plus pressure head)
- *Pressure
- *Water Quality
Link parameters available for viewing include:
- Length
- Diameter
- Roughness Coefficient
- Bulk Reaction Coefficient
- Wall Reaction Coefficient
- *Flow Rate
- *Velocity
- *Headloss (per 1000 feet (or meters) of pipe)
- *Friction Factor (as used in the Darcy-Weisbach headloss formula)
- *Reaction Rate (average over length of pipe)
- *Water Quality (average over length of pipe)
The items marked with asterisks are computed quantities whose values will only be available if a successful analysis has been run on the network (see Chapter Analyzing a Network).
7.2. Setting the Map’s Dimensions¶
The physical dimensions of the map must be defined so that map coordinates can be properly scaled to the computer’s video display. To set the map’s dimensions:
- Select View >> Dimensions.
- Enter new dimension information into the Map Dimensions dialog that appears (see Fig. 7.1) or click the Auto-Size button to have EPANET compute dimensions based on the coordinates of objects currently included in the network.
- Click the OK button to re-size the map.
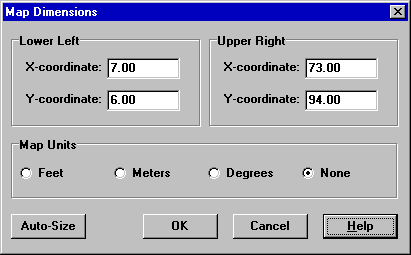
Fig. 7.1 Map dimensions dialog.
The information provided in the Map Dimensions dialog consists of the following (Table 7.1):
| ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Lower Left Coordinates | The X and Y coordinates of the lower left point on the map. |
| Upper Right Coordinates | The X and Y coordinates of the upper right point on the map. |
| Map Units | Units used to measure distances on the map. Choices are Feet, Meters, Degrees, and None (i.e., arbitrary units). |
Note: If you are going to use a backdrop map with automatic pipe length calculation, then it is recommended that you set the map dimensions immediately after creating a new project. Map distance units can be different from pipe length units. The latter (feet or meters) depend on whether flow rates are expressed in US or metric units. EPANET will automatically convert units if necessary.
7.3. Utilizing a Backdrop Map¶
EPANET can display a backdrop map behind the pipe network map. The backdrop map might be a street map, utility map, topographic map, site development plan, or any other picture or drawing that might be useful. For example, using a street map would simplify the process of adding pipes to the network since one could essentially digitize the network’s nodes and links directly on top of it (Fig. 7.2).
Fig. 7.2 Example backdrop.
The backdrop map must be a Windows enhanced metafile or bitmap created outside of EPANET. Once imported, its features cannot be edited, although its scale and extent will change as the map window is zoomed and panned. For this reason metafiles work better than bitmaps since they will not loose resolution when re-scaled. Most CAD and GIS programs have the ability to save their drawings and maps as metafiles.
Selecting View >> Backdrop from the Menu Bar will display a sub-menu with the following commands:
- Load (loads a backdrop map file into the project)
- Unload (unloads the backdrop map from the project)
- Align (aligns the pipe network with the backdrop)
- Show/Hide (toggles the display of the backdrop on and off)
When first loaded, the backdrop image is placed with its upper left corner coinciding with that of the network’s bounding rectangle. The backdrop can be re-positioned relative to the network map by selecting View >> Backdrop >> Align. This allows an outline of the pipe network to be moved across the backdrop (by moving the mouse with the left button held down) until one decides that it lines up properly with the backdrop. The name of the backdrop file and its current alignment are saved along with the rest of a project’s data whenever the project is saved to file.
For best results in using a backdrop map:
- Use a metafile, not a bitmap.
- Dimension the network map so that its bounding rectangle has the same aspect ratio (width-to-height ratio) as the backdrop.
7.4. Zooming the Map¶
To Zoom In on the map:
- Select View >> Zoom In or click
on the Map Toolbar.
- To zoom in 100%, move the mouse to the center of the zoom area and click the left button.
- To perform a custom zoom, move the mouse to the upper left corner of the zoom area and with the left button pressed down, draw a rectangular outline around the zoom area. Then release the left button.
To Zoom Out on the map:
- Select View >> Zoom Out or click
on the Map Toolbar.
- Move the mouse to the center of the new zoom area and click the left button.
- The map will be returned to its previous zoom level.
7.5. Panning the Map¶
To pan the map across the Map window:
- Select View >> Pan or click
on the Map Toolbar.
- With the left button held down over any point on the map, drag the mouse in the direction you wish to pan in.
- Release the mouse button to complete the pan.
To pan using the Overview Map (which is described in Section 7.8 below):
- If not already visible, bring up the Overview Map by selecting View>> Overview Map.
- Position the mouse within the zoom window displayed on the Overview Map.
- With the left button held down, drag the zoom window to a new position.
- Release the mouse button and the main map will be panned to an area corresponding to that of the Overview Map’s zoom window.
7.6. Finding an Object¶
To find a node or link on the map whose ID label is known:
- Select View >> Find or click
on the Standard Toolbar.
- In the Map Finder dialog box that appears, select Node or Link and enter an ID label.
- Click Find.
If the node/link exists it will be highlighted on the map and in the Browser. If the map is currently zoomed in and the node/link falls outside the current map boundaries, the map will be panned so that the node/link comes into view. The Map Finder dialog will also list the ID labels of the links that connect to a found node or the nodes attached to a found link.
To find a listing of all nodes that serve as water quality sources:
- Select View >> Find or click
on the Standard Toolbar.
- In the Map Finder dialog box that appears, select Sources.
- Click Find.
The ID labels of all water quality source nodes will be listed in the Map Finder. Clicking on any ID label will highlight that node on the map.
7.7. Map Legends¶

Fig. 7.3 Example map legend.
There are three types of map legends that can be displayed. The Node and Link Legends associate a color with a range of values for the current parameter being viewed on the map (see Fig. 7.3). The Time Legend displays the clock time of the simulation time period being viewed. To display or hide any of these legends check or uncheck the legend from the View >> Legends menu or right- click over the map and do the same from the popup menu that appears. Double-clicking the mouse over it can also hide a visible legend.
To move a legend to another location:
- Press the left mouse button over the legend.
- With the button held down, drag the legend to its new location and release the button.
To edit the Node Legend:
- Either select View >> Legends >> Modify >> Node or right-click on the legend if it is visible.
- Use the Legend Editor dialog form that appears (see Fig. 7.4) to modify the legend’s colors and intervals.
A similar method is used to edit the Link Legend.
The Legend Editor (Fig. 7.4) is used to set numerical ranges to which different colors are assigned for viewing a particular parameter on the network map. It works as follows:
- Numerical values, in increasing order, are entered in the edit boxes to define the ranges. Not all four boxes need to have values.
- To change a color, click on its color band in the Editor and then select a new color from the Color Dialog box that will appear.
- Click the Equal Intervals button to assign ranges based on dividing the range of the parameter at the current time period into equal intervals.
- Click the Equal Quantiles button to assign ranges so that there are equal numbers of objects within each range, based on values that exist at the current time period.
- The Color Ramp button is used to select from a list of built-in color schemes.
- The Reverse Colors button reverses the ordering of the current set of colors (the color in the lowest range becomes that of the highest range and so on).
- Check Framed if you want a frame drawn around the legend.
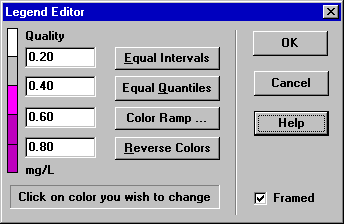
Fig. 7.4 Legend editor dialog.
7.8. Overview Map¶
The Overview Map allows you to see where in terms of the overall system the main network map is currently focused. This zoom area is depicted by the rectangular boundary displayed on the Overview Map (Fig. 7.5). As you drag this rectangle to another position the view within the main map will follow suit. The Overview Map can be toggled on and off by selecting View >> Overview Map. Clicking the mouse on its title bar will update its map image to match that of the main network map.
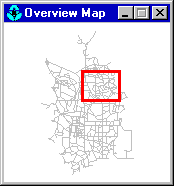
Fig. 7.5 Example of overview map.
7.9. Map Display Options¶
There are several ways to bring up the Map Options dialog form (Fig. 7.6) used to change the appearance of the Network Map:
- Select View >> Options
- Click the Options button
on the Standard Toolbar when the Map window has the focus
- Right-click on any empty portion of the map and select Options from the popup menu that appears
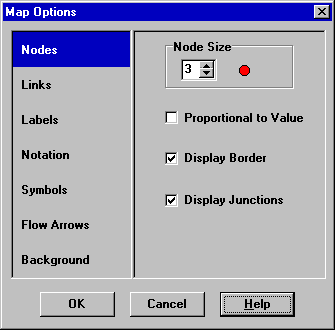
Fig. 7.6 Map options dialog.
The dialog contains a separate page, selected from the panel on the left side of the form, for each of the following display option categories:
- Nodes (controls size of nodes and making size be proportional to value)
- Links (controls thickness of links and making thickness be proportional to value)
- Labels (turns display of map labels on/off)
- Notation (displays or hides node/link ID labels and parameter values)
- Symbols (turns display of tank, pump, valve symbols on/off)
- Flow Arrows (selects visibility and style of flow direction arrows)
- Background (changes color of map’s background)
Node Options
The Nodes page of the Map Options dialog controls how nodes are displayed on the Network Map (Table 7.2).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Node Size | Selects node diameter |
| Proportional to Value | Select if node size should increase as the viewed parameter increases in value |
| Display Border | Select if a border should be drawn around each node (recommended for light-colored backgrounds) |
| Display Junctions | Displays junction nodes (all junctions will be hidden unless this option is checked). |
Link Options
The Links page of the Map Options dialog controls how links are displayed on the map (Table 7.3).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Link Size | Sets thickness of links displayed on map |
| Proportional to Value | Select if link thickness should increase as the viewed parameter increases in value |
Label Options
The Label page of the Map Options dialog controls how labels are displayed on the map (Table 7.4).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Display Labels | Displays map labels (labels will be hidden unless this option is checked) |
| Use Transparent Text | Displays label with a transparent background (otherwise an opaque background is used) |
| At Zoom Of | Selects minimum zoom at which labels should be displayed; labels will be hidden at zooms smaller than this unless they are meter labels |
Notation Options
The Notation page of the Map Options dialog form determines what kind of annotation is provided alongside of the nodes and links of the map (Table 7.5).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Display Node IDs | Displays node ID labels |
| Display Node Values | Displays value of current node parameter being viewed |
| Display Link IDs | Displays link ID labels |
| Display Link Values | Displays values of current link parameter being viewed |
| Use Transparent Text | Displays text with a transparent background (otherwise an opaque background is used) |
| At Zoom Of | Selects minimum zoom at which notation should be displayed; all notation will be hidden at zooms smaller than this |
Note: Values of the current viewing parameter at only specific nodes and links can be displayed by creating Map Labels with meters for those objects. See Section 6.2 and Section 6.4 as well as Table 6.7.
Symbol Options
The Symbols page of the Map Options dialog determines which types of objects are represented with special symbols on the map (Table 7.6).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Display Tanks | Displays tank symbols |
| Display Pumps | Displays pump symbols |
| Display Valves | Displays valve symbols |
| Display Emitters | Displays emitter symbols |
| Display Sources | Displays + symbol for water quality sources |
| At Zoom Of | Selects minimum zoom at which symbols should be displayed; symbols will be hidden at zooms smaller than this |
Flow Arrow Options
The Flow Arrows page of the Map Options dialog controls how flow-direction arrows are displayed on the network map (Table 7.7).
| OPTION | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Arrow Style | Selects style (shape) of arrow to display (select None to hide arrows) |
| Arrow Size | Sets arrow size |
| At Zoom Of | Selects minimum zoom at which arrows should be displayed; arrows will be hidden at zooms smaller than this |
Note: Flow direction arrows will only be displayed after a network has been successfully analyzed (see Section 8.2).
Background Options
The Background page of the Map Options dialog offers a selection of colors used to paint the map’s background with.